Member Connection Troubleshooting Guide
Step 1 - Confirming Connections and Power:
First of all, we need to make sure all the indoor devices of your mesh install are connected properly.
Most installs have the standard equipment shown here but not every building is the same. If your equipment looks different than what's show here, please reach out to us for further assistance via out website or on #support on Slack.
How your equipment should be connected varies, however here are the most common setups you may have in your apartment.
Omni POE Injector with TP-Link Router:
This is the most common setup for mesh nodes. The problem points to check are as follows:
- Ensure both power supplies are plugged into a working outlet on the wall.
- The POE power adapter has a green light to indicate it is on and working.
- The POE and router power supplies are not interchangeable (pay attention to the larger and smaller sizes).
- Ensure the cable coming from the roof is securely plugged into the POE Injector. Unplug it, check for damage/corrosion on the plug and reconnect it. (This will restart the rooftop antenna)
- Ensure the other cables are firmly connect to the POE Injector.
- Ensure the short network cable or POE Injector is plugged into the Blue Port on the back of the router. (Not the orange ones!)
- Ensure the router power supply is plugged in securely to the router. Ensure the power button on the back of the router is pressed in.
In buildings with multiple apartments connected to the mesh, some apartments may only have the TP-Link router and no POE Injector. In this case, confirm the cable from the roof is plugged into the router and the router has power.
If you still don't have internet, you may need to visit/ask your neighbor to confirm who has the POE injector and if it's properly connected in their apartment as well.
Fiber Connected Apartments (Grand St, Olmstead, Belmont Cove):
Fiber connected buildings such as Olmstead, the Grand St Guild Complex and Belmont Cove use apartment hardware that is similar to this.
Troubleshooting steps include the following:
- Ensure that the power supply is plugged into a working outlet.
- Check that the fiber connection is plugged in. Avoid unplugging or reconnecting the fiber unless told to do so.
- Examine the fiber running through your apartment looking for any damage, cuts or sharp bends / kinks.
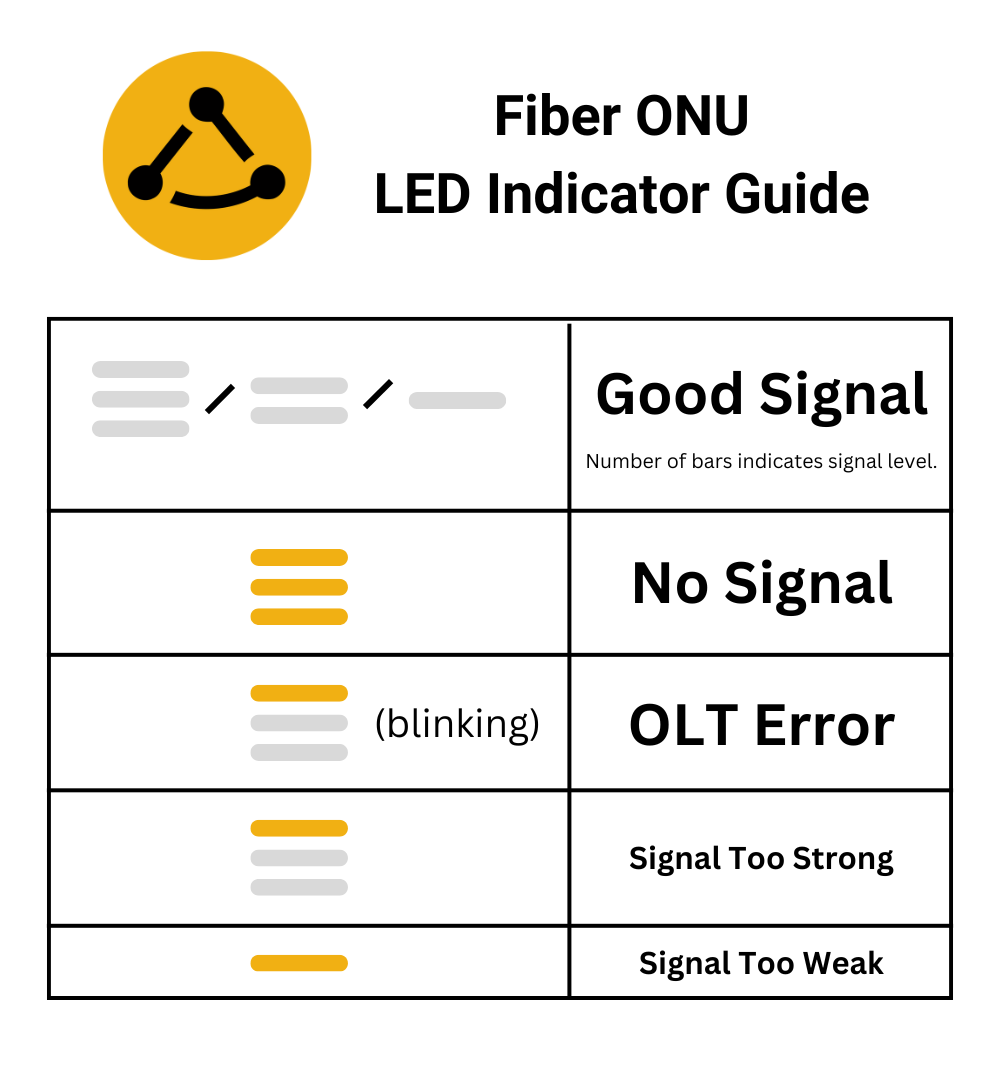
- Examine the LEDs on the fiber unit to determine if there's a signal issue. The LED codes are as follows:
- If any orange lights are present, please reach out to us for further assistance.
Second step:
Test the connection, eliminating the router and WiFi.
To test without WiFi, connect your computer directly to the router using an ethernet patch cable. Turn WiFi off on your computer to make sure you are using the cable and not WiFi.
To check if the router is the issue, connect directly to the POE, bypassing the router altogether.
If possible, connect your devices with ethernet cables to your router. An Ethernet connection will be faster and more reliable than a WiFi connection.
Third step:
Try power-cycling the equipment.
Start with the router: unplug it from wall power and a wait few seconds for all the lights to go out. Then plug it back in.
If you have a POE you can also try unplugging the POE and replugging after a few seconds. Note that this will distrupt anyone connected to the same equipment.
Other things to try:
Keeping your router's firmware up to date ensures that you benefit from bugfixes or security enhancements.
Your Internet and WiFi Speeds
How much speed do you need?
Several factors can affect your internet performance: WiFi router location, number of users, the hardware and age of your device(s), the device software (called firmware), and any applications running in the background of your computer.
There is a perception that Internet services require a lot of bandwidth (speed). Recommended internet speeds for use of third-party products and services depend on the number of devices you're using. See the following speeds required for these common third-party products and services:
-- Streaming HD 10 Mbps
-- Skype Call HD 1.5 Mbps
-- Video Gaming 3.5 Mpbs
-- Twitch Gaming 4.5-6 Mbps
-- Netflix 5 Mbps
-- Amazon Prime HD 15 Mbps
For more information please refer to each service's website, or consult the FCC's Broadband Speed Guide.
WiFi Router Location
If you’re connecting to the Internet via WiFi, make sure your router is placed as close to the middle of your home as possible, away from obstructions (such as cabinets), away from other electronic devices, and off the floor. Walls, metal (ductwork or decking), refrigerators, and microwave ovens, reduce signal if not block it totally. Electronic devices (microwaves, TVs, baby monitors, cordless phones, etc.) can create interference. Wi-Fi doesn’t do well around lots of water, either, so stay away from aquariums and domaestic water heaters.
Wifi band
WiFi routers operate in different frequencies. The 5 GHz wireless frequency provides faster data rates at shorter distances and is typically much less "busy" than the 2.4 GHz wireless frequency. If wireless range is your priority, 2.4 GHz performs better than 5 GHz, but 2.4 Ghz is more susceptible to interference. The 5 GHz wireless frequency doesn’t penetrate solid objects nearly as well as the 2.4 GHz. A dual-band router (2.4/5 Ghz) usually performs better than a mono-band 2.4Ghz router, as your device (smartphone, laptop) will choose the better signal, 2.4 or 5 Ghz.
Make sure your old or slow devices, e.g., printers, use the 2.4Ghz to free up the 5Ghz.
-
Note 1: WiFi 6 and 6 Ghz
WiFi 6 referes to the new standard 802.11ax (or AX WiFi). It works on 2.4, 5, or the newly open band 6 Ghz. WiFi 6 ≠ 6 Ghz The WiFi 6 improvement will not only affect 5GHz networks, which the industry has largely shifted to, and which provide faster data on shorter distances; it will also make 2.4GHz networks faster, which are typically slower but better at penetrating solid objects like walls. -
Note 2: the 5GHz band has nothing to do with 5G cellular service - two differents things. 5G refers to the 5th generation mobile network for cellular phones.
Wifi channels
Wifi operates on different channels (like cars driving on different lanes of a highway). Your neighbor's router may operate on the same channel as your router, creating congestion. Try to change your router's WiFi channel. There are apps that can scan the airwaves and tell you which channels are the least occupied. Channel occupation, just like road traffic, depends on time of day and may change from one day to another, as your neighbors may just do the same, change channel.
Test the performance
It is a good idea to always use the same tool to test to be able to compare. We use speedtest.net against Pilot Fiber, New York, NY as the server.