MikroTik OmniTik 5 POE AC
The Omnitik 5ac is an outdoor switch/router with a built-in 5Ghz 802.11ac access point, omnidirectional antenna, and 5 gigabit ethernet ports. Be sure to get the POE version.
The OmniTik serves as a central rooftop router with several purposes:
- As a switch to connect multiple apartments or other rooftop devices (LiteBeam, SXTs etc.)
- Can output POE power to power LiteBeams or other antennas.
- It acts as an WiFi Access Point for the rooftop, and runs our config of WDS and OSPF so it will mesh with other OmniTiks or SXTsqs within a few blocks
- Provides remote management, a console interface and allows speed/traceroute/ping testing of the hub.
Please be sure to see MikroTik Specifics for extra info about Mikrotik devices, how to connect, etc.

The PoE version accepts 12-57V passive PoE on port 1 and can be configured to provide PoE out to ports 2-5.
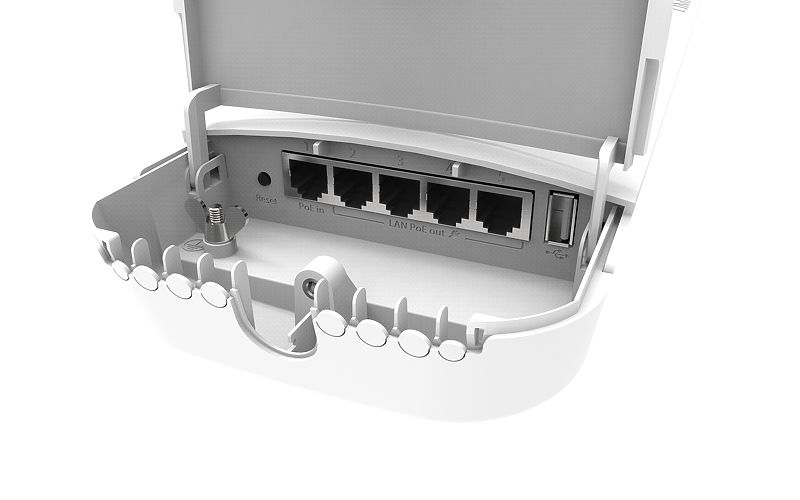

The small round plastic tabs, shown in the picture above, should be removed for those cable ports you will use - push them firmly inwards to remove. Leave the tabs in unused ports to prevent water/critter entry.
Device specs are available at Mikrotik.com
Uses
- Hub node routing or AP ( for standard 802.11ac hubs )
- Rooftop installations for multi-tenant houses
- Providing public access via the omnidirectional antenna
How to reset
- Press reset
- Apply power
- Watch the power led, once it blinks, STOP pressing the reset button
- It will beep one time
- Once you hear two beeps, you should be able to access it.
How to upgrade the firmware
- Upload the routeros-mipsbe-x.x.x.npk file in http://192.168.88.1/webfig/#Files
- Select System Reboot
How to downgrade firmware
- Upload the routeros-mipsbe-x.x.x.npk file in http://192.168.88.1/webfig/#Files
- Go to Terminal and type
/system package downgrade;
Configuration Instructions
You can configure Mikrotik devices either with Winbox graphical interface (Scroll Down) or with a CLI (terminal) interface.
Omnitik Configuration with Terminal
Here is a slideshow guide of configuring an OmniTik.
1. Download Stable Firmware and Generate Configuration
Don't use version 7 of firmware. It won't work with the configgen file! Make sure your firmware is v6.x.x.
You will need your Network Number or NN. You can find out your NN using your Install Number (request number) received by email when you registered. To find out what is your NN please see Network Number.
If you do not have a NN (the tool returns "No NN assigned") please reach out on Slack to have one assigned to you.
- Download the latest stable v6 firmware - see Mikrotik Firmware for the currently recommended version.
- Generate a configuration file for your Network Number by going to the NYC Mesh configuration generator.
- Confirm you have selected the correct device and version of the config file.
- Type in your Network Number (NN).
2. Connect to the Router
- To connect to the Omnitik wirelessly, find the router’s default SSID (Mikrotik-XXXX) and connect to it.
- To connect with a cable, plug one end of a patch cable into the Omnitik’s Port 2 and the other end into your computer’s LAN port. Set your computer to DHCP (automatic) and it will get an address like 192.168.88.xxx.
- Navigate to the default Mikrotik IP of 192.168.88.1 in your web browser. This will open the Mikrotik GUI. The default username is admin and there is no password.
3. Upload Firmware
- Open the Mikrotik GUI in your browser.
- Click “Webfig” in the top right corner.
- Click “Files” in the left side menu.
- Click “Choose File” at the top.
- Navigate to where you saved the firmware, select the file and click “Open”. You will see the file appear in the interface.
- Wait for the firmware to fully upload (you will see the upload progress in the bottom left corner). This firmware will automatically be installed when you reboot with the new configuration (see next section).
4. Upload Configuration
- If you are using a Mac or Linux operating system, go into Terminal, navigate to the folder where you’ve saved the config and enter the following command:
scp -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no omni-poe-ether5.rsc admin@192.168.88.1:flash/- If you are using a Windows operating system, go into Command Prompt, navigate to the folder where you’ve saved the config and enter the following command. You must download pscp.exe from PuTTY (64-bit or 32-bit) to the same folder then run:
pscp -scp omni-poe-ether5.rsc admin@192.168.88.1:flash/If asked “Dangerous Reset anyway?”, type in Y and return/enter.
Reopen the Mikrotik GUI in your web browser and navigate back to “Files” as described in section 3 above. You should see the config file you just uploaded.
-
- Click “System” in the left side menu.
- Click “Reset Configuration” in the left side menu dropdown. Select the following options:
- No Default Configuration
- Run After Reset: flash/rooftop-ospf.rsc (click the popup on the right to select this)
- Click "Reset Configuration"
- The Omnitik will now reboot (and install new firmware if you uploaded it). If it plays some beeps, ending with a short tune Kernkraft 400, the configuration was a success!
The Omnitik IP address has changed to a 10.69.x.x address. This is generated from the network number, e.g. for network number 1234 the IP address will be 10.69.12.34. Please see Network Number for additional information about finding your devices IP if needed.
5. Change the Password
- Click “System” in the left side menu, then click “Password”.
- Leave the "Current Password" blank and enter the standard omni password in "New Password" and "Confirm Password".
6. Confirm POE output is on if required
Most installs have a LiteBeam or other device that's connected to the Omni. This device uses power from the omni's port, so POE out on that port must be turned on. Typically a LiteBeam is connected to Port 5, so POE out must be turned on for ether5.
If you used the omni-poe-ether5 template on configgen, this will already be done for you.
- Click on "Interfaces" in the left sidebar menu.
- Click on ether-5 (or whichever port the device that needs power is on)
- Set "POE Out" to "forced on"
Omnitik Configuration with Winbox
You can configure OmniTik routers and all MikroTik equipment with their WinBox software and associated apps.
1. Download WinBox for your device:
First you will need to download a WinBox-compatible client to configure the OmniTik.
Desktop (Windows, Mac OS, Linux)
Download the WinBox utility from the MikroTik website. There are stable versions for Windows and beta version that are native for Mac OS and Linux.
Open the utility and click the "Neighbors" tab on the lower-half of the screen, and click "Refresh".
Double-click on the MAC Address (important!) that appears in the list. When the MAC Address populates into the "Connect To" box, hit "Connect".
You will get a prompt saying "RouterOS Default Configuration". Hit OK to dismiss.
On the left sidebar, click "Files". Open a File Explorer or Finder window alongside winbox and and drop the configuration file you downlaoded earlier into the "flash" folder. You should see the uploaded file have flash/ before the filename (important! if it doesn't have flash before it, make sure you drop the file onto the flash folder and try again).
On the left sidebar, click "System", then "Reset Configuration". Check the "No Default Configuration" box, and click the down arrow next to "Run After Reset" to select the file you uploaded. Finally, hit "Reset Configuration" and you will be disconnected. After a couple of minutes, the LED next to the person icon on the device will turn on, indicating that the configuration has been applied.
Mobile (Android)
The MikroTik Pro app uses the same WinBox protocol to upload files and configure your router without a computer. You can download it from the Play Store.
Mobile (iOS / Apple Devices)
The MikroTik app uses the same WinBox protocol to upload files and configure your router without a computer. You can download it from the App Store.
2. Download Stable Firmware and Generate Configuration
Don't use version 7 of firmware. It won't work with the configgen file! Make sure your firmware is v6.x.x.
You will need your Network Number or NN. You can find out your NN using your Install Number (request number) received by email when you registered. To find out what is your NN please see Network Number.
If you do not have a NN (the tool returns "No NN assigned") please reach out on Slack to have one assigned to you.
- Download the latest stable v6 firmware - see Mikrotik Firmware for the currently recommended version.
- Generate a configuration file for your Network Number by going to the NYC Mesh configuration generator.
- Confirm you have selected the correct device (Omnitik5AC) and version of the config file (omni-only or omni-poe-ether5).
- Type in your Network Number (NN).
- Note the downloaded file with your config, ending in .rsc
- Confirm you have selected the correct device (Omnitik5AC) and version of the config file (omni-only or omni-poe-ether5).
2. Connect to the router
You can connect to the router using an Ethernet cable or through Wi-Fi. There are caveats to both, but configuring wirelessly is the easiest to do when doing the install outside.
Wired
Assuming your Ethernet adapter is setup to get an IP from the router using DHCP (probably default), all you have to do is plug an Ethernet cable from your computer to a Port 2-4 on the router.
Do NOT plug the computer into the PoE injector (Port 1) as the default configuration blocks all inbound connections to this port, including WinBox.
Do NOT plug the computer into Port 5, as we may be configuring this later to do PoE-Out which will damage any devices plugged in here that are not expecting power.
Wireless
Assuming your Wi-Fi adapter is setup to get an IP from the router using DHCP (probably default), all you have to do is look for a network in your Wi-Fi settings named MikroTik-xxxxx. This network will only appear after the router has fully powered on (two short beeps).
If you are on a phone, sometimes you will have to turn off your Mobile data/turn on airplane mode in order to reach the router that technically does not have any internet yet.
Make sure any VPN software you have is disabled at this point, as it will likely block any connections to the router.
From your WinBox software, find the "Neighbors" tab on the lower-half of the screen. On the MikroTik app, click on the "Discover" tab. You should see an entry on the list with Identity MikroTik. If you do not see anything, click "Refresh" or swipe down to rescan for devices. Double-check your connections and confirm you are getting an IP from the router (will be in the 192.168.88.*** range).
Double-click or tap on the entry to load the IP into the software. On the App, you will be prompted to select either MAC or IP; select IP. Now, the default login admin/[no password] will be displayed and you can hit "Connect".
You will get a prompt saying "RouterOS Default Configuration". Hit OK to get out of here (do NOT remove configuration or use quick setup). Now for the fun part.
3. Upload the configuration
From your WinBox software, drag and drop the firmware routeros-mipsbe-***.npk file into the blank space in the window. You should see the file transfer take a few seconds before it finishes. Next, drag and drop the rooftop-ospf.rsc file onto the flash folder. You should see the uploaded file labeled flash/rooftop-ospf.rsc.
From your phone, hit the upload arrow button on the bottom-left of the screen and select the routeros-mipsbe-***.npk file. You can save as the original name and hit OK. You should see the file transfer take a few seconds before it finishes. Next, do the same with the rooftop-ospf.rsc file, but this time make sure you prepend the file name with flash/ and hit OK. You should see the uploaded file labeled flash/rooftop-ospf.rsc.
4. Flash the config and party
5. Confirm settings and configuration
WinBox will inform you that the router has been disconnected. Hit Cancel. If you are connecting wirelessly, look in your Wi-Fi settings for nycmesh-****-omni. Connect to that wireless network with the password nycmeshnet. If you are connecting via Ethernet, you can test this on another device to make sure the Wi-Fi is working correctly. If you are not planning on adding devices or changing the configuration further, you are done! 🎉
If you are planning on connecting a LiteBeam to your router or just want to learn about the configuration, go back to "Neighbors" or "Discover" depending on your platform; you should see an entry on the list with Identity "nycmesh-****-omni". Login to it like before.
Wireless interface explanation
With the default NYC Mesh configuration loaded, the OmniTik transmits a number of wireless networks.
To see these networks, go to "Wireless" in the left sidebar menu.
Here's what each of these networks does:
wlan1- SSID example:
nycmesh-136-omni - AP bridge (MikroTik term)
- manually connected to by other Omni's to avoid route flapping behavior exhibited by the automatic mesh (
wlan3)
- SSID example:
wlan2- SSID example:
-NYC Mesh Community WiFi- - Also ap bridge
- only difference to
wlan1is bridge filter and and ip firewall rule
- SSID example:
wlan3- SSID example:
nycmesh-wds - wds slave
- all automatic mesh connections communicate through this interface
- wds bridge
- is not running a dhcp server
- OSPF will route to other connections first since bridge for this interface is higher at 100
- SSID example:
wlan4- station bridge for connecting to another omni's access point. (That Omni's wlan1 interface)
- has a lower cost of 10 versus the WDS interface. This allows you to force another Omni to be the uplink, overriding the dynamic wds routing. This prevents the Omni from "flapping" between several nearby Omni's.
- station bridge for connecting to another omni's access point. (That Omni's wlan1 interface)
Expand for `OLD nycmesh-omnitik-v3.2.rsc` example
The is our obsolete 3.2 template script which needs some variables filled in.
This script only works on the OmniTik 5ac PoE model
Version 3.2 Changelog:
- Separation of Public vs Tenant subnet
- Fixed BGP sync missed config parameter
- Startup delay ( ref Mikrotik forums )
- Tada sound effect
- Better firewall rules
:global nodenumber 1111
:global bgpasn 61111
:global ipprefix "10.70.111"
:global iptenantsrange 10.70.111.5-10.70.111.119
:global iptenantsgw 10.70.111.1
:global ippublicrange 10.70.111.130-10.70.111.180
:global ippublicgw 10.70.111.129
:global dns 10.10.10.10,1.1.1.1
/delay 15
:for j from=1 to=4 step=1 do={ :for i from=2000 to=50 step=-400 do={ :beep frequency=$i length=11ms; :delay 11ms; } :for i from=800 to=2000 step=400 do={ :beep frequency=$i length=11ms; :delay 11ms; } }
:foreach x in=[/interface wireless find] do={ /interface wireless reset-configuration $x }
:for t from=1200 to=350 step=-50 do={ :beep frequency=$t length=33ms; :delay 33ms; }
:beep frequency=500 length=100ms
/ip address add address=192.168.88.1/24 interface=ether3 network=192.168.88.0
:beep frequency=600 length=100ms
/interface ethernet set [ find default-name=ether5 ] poe-out=forced-on
:beep frequency=700 length=100ms
/interface wireless security-profiles add authentication-types=wpa-psk,wpa2-psk management-protection=allowed mode=
dynamic-keys name=nycmeshnet supplicant-identity=nycmesh
wpa-pre-shared-key=nycmeshnet wpa2-pre-shared-key=nycmeshnet
:beep frequency=800 length=100ms
/interface wireless set [ find default-name=wlan1 ] band=5ghz-a/n/ac channel-width=20/40/80mhz-Ceee disabled=no distance=indoors frequency=auto mode=ap-bridge security-profile=nycmeshnet ssid=("nycmesh-" . $nodenumber . "-omni") wireless-protocol=802.11 wps-mode=disabled add disabled=no master-interface=wlan1 name=wlan2 ssid="-NYC Mesh Community WiFi-" wps-mode=disabled
:beep frequency=900 length=100ms
/interface bridge add auto-mac=yes name=publicaccess add auto-mac=yes name=tenants
:beep frequency=1000 length=100ms
/ip address add address=($ipprefix . ".1/25") interface=tenants network=($ipprefix . ".0") add address=($ipprefix . ".129/26") interface=publicaccess network=($ipprefix . ".128")
:beep frequency=1100 length=100ms
/interface bridge port add bridge=tenants interface=ether1 add bridge=tenants interface=ether2 add bridge=tenants interface=ether3 add bridge=tenants interface=ether4 add bridge=tenants interface=wlan1 add bridge=publicaccess interface=wlan2
:beep frequency=1200 length=100ms
/ip pool add name=tenants ranges=$iptenantsrange add name=publicaccess ranges=$ippublicrange
:beep frequency=1300 length=100ms
/ip dhcp-server add address-pool=tenants disabled=no interface=tenants name=tenantsdhcp add address-pool=publicaccess disabled=no interface=publicaccess name=publicaccessdhcp
:beep frequency=1400 length=100ms
/routing bgp instance set default as=$bgpasn disabled=no
:beep frequency=1500 length=100ms
/routing bgp network add network=($ipprefix . ".0/24") synchronize=no
:beep frequency=1600 length=100ms
/ip dhcp-server network add address=($ipprefix . ".0/25") dns-server=10.10.10.10 gateway=($ipprefix . ".1") netmask=25 add address=($ipprefix . ".128/26") dns-server=10.10.10.10 gateway=($ipprefix . ".129") netmask=25
:beep frequency=1700 length=100ms
/ip firewall filter add action=accept chain=input protocol=icmp add action=drop chain=forward in-interface=publicaccess out-interface=tenants add action=drop chain=input in-interface=publicaccess add action=accept chain=forward add action=accept chain=input
:beep frequency=1800 length=100ms
/system clock set time-zone-name=America/New_York
/system identity set name=("nycmesh-" . $nodenumber . "-omni")
:beep frequency=500 length=200ms;
:delay 500ms;
:beep frequency=500 length=200ms;
:delay 200ms;
:beep frequency=800 length=500ms;
:delay 50ms;How to apply config:
- Acquire config parameters ( BGP ASN, IP range, node number, etc. )
- Fill in config file parameters at the top of the script.
Save as nycmesh-omni-####.rsc where #### is your node number.
The file must be named with.rscat the end.
- Factory Reset device if needed ( see MikroTik Specifics for details )
( Connect to a port besides Port 1 ) - Update firmware to latest on your device ( see Mikrotik Firmware )
- Upload the rsc file
- The file needs to be in the
flash/folder. However, there is no way to create a folder from the device. - Instead you need to upload the file using scp.
- From a Mac or Linux desktop, upload the file using scp:
scp nycmesh-omni-####.rsc admin@192.168.88.1:flash/
You may need to confirm the SSH key ( typical with SSH ) - From a Windows desktop, you must have PuTTY installed and run the following command from the command prompt:
pscp -scp nycmesh-omni-####.rsc admin@192.168.88.1:flash/ - You should see the file in the WebUI as
flash/nycmesh-omni-####.rsc
- The file needs to be in the
- Factory Reset the device with the option to restore this script.
- From Web UI:
- WebFig > System > Reset Configuration. Select:
- No Defaults
- Run After Reset:
flash/nycmesh-omni-####.rsc - Apply
- Or from CLI:
/system reset-configuration run-after-reset=flash/nycmesh-omni-####.rsc no-defaults=yes- Dangerous Reset anyway? Y
- From Web UI:

No comments to display
No comments to display